Smart Building implementation (percentage of the total floor area of smart building to the total all floors building area
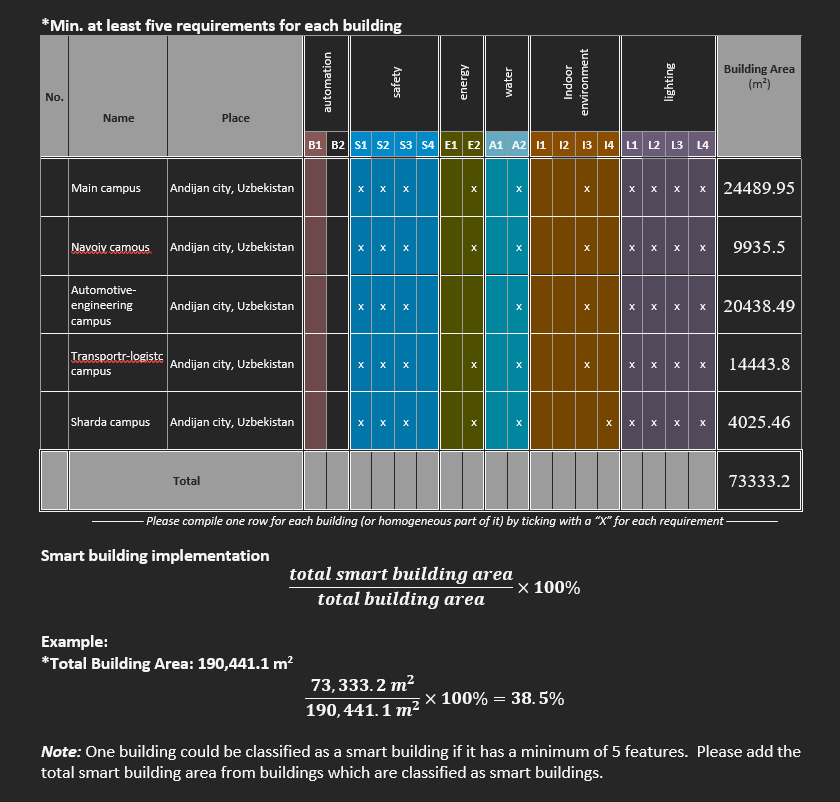

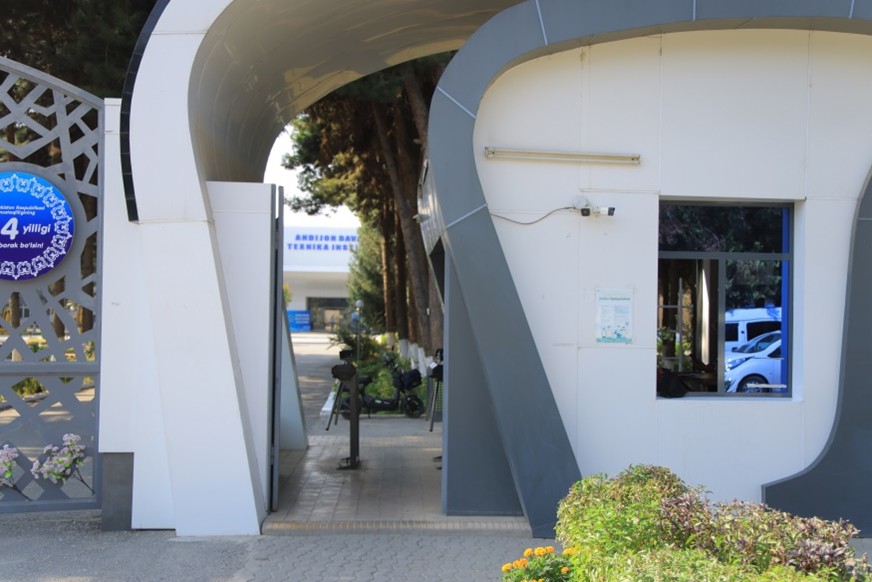
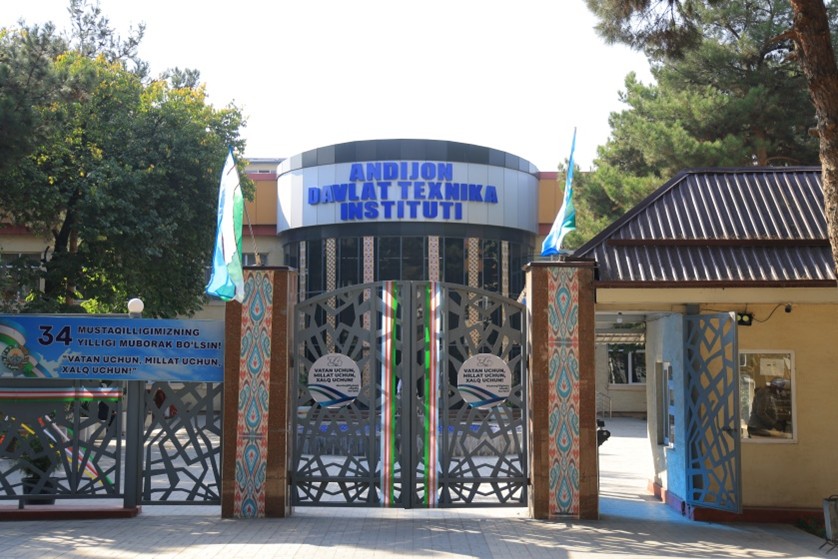
Main Campus

Navoiy campus

Automotive engineering campus

Transport logistcs campus
Smart Building Implementation in Andijan State Technical Institute Campuses
At Andijan State Technical Institute (AndMI), the Smart Building Implementation initiative aims to modernize all five campuses by integrating advanced information and communication technologies (ICT) with sustainable infrastructure solutions. This program focuses on enhancing energy efficiency, improving comfort, and reducing the environmental footprint of campus facilities.
1. Main Campus (Academic and Administrative Center)
The Main Campus of Andijan State Technical Institute serves as the heart of academic and administrative operations. Within the framework of the Smart Building Implementation initiative, the campus has been equipped with a centralized Building Management System (BMS) designed to optimize energy usage and enhance sustainability.
The system integrates smart lighting, automated HVAC control, and energy monitoring dashboards. Motion and light sensors automatically adjust indoor lighting based on occupancy and daylight intensity, while temperature regulation systems maintain optimal comfort with minimal energy waste.
In addition, all administrative buildings are fitted with smart meters that track real-time power and water consumption, allowing facility managers to make data-driven decisions for conservation. Digital dashboards display usage analytics, promoting transparency and awareness among both students and staff.
Through these innovations, the Main Campus has achieved a measurable reduction in electricity and water use, contributing directly to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
2. Automotive - Engineering Campus
The automotive Engineering Campus plays a crucial role in integrating innovation and sustainability within the institute’s technical disciplines. As part of the Smart Building Implementation program, this campus has been transformed into a model of intelligent infrastructure that supports both academic and research activities.
The laboratories and workshops are equipped with smart ventilation systems and automated air-quality monitoring sensors to ensure a healthy and efficient learning environment. Energy-efficient LED systems are installed across all facilities, operating under motion-based control mechanisms to minimize unnecessary electricity usage.
Moreover, the campus has introduced a digital maintenance management system (DMMS) that tracks equipment performance and schedules predictive maintenance. This reduces downtime, conserves resources, and extends the lifespan of machines and laboratory tools.
To further promote sustainable engineering practices, solar-powered stations and digital energy meters have been installed around the campus, helping to track renewable energy contribution in real time. These initiatives strongly align with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
3. Navoiy Campus
The Navoiy Campus stands as the digital transformation hub of the institute, where cutting-edge technology and sustainability intersect. Under the Smart Building Implementation initiative, this campus has been equipped with an integrated Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure that connects lighting, climate control, and security systems into a unified digital network.
All classrooms and laboratories utilize automated environmental control systems that monitor temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels, ensuring both comfort and energy efficiency. Smart LED lighting adjusts dynamically according to occupancy and natural light intensity, reducing power consumption significantly.
The campus also hosts an Energy Management and Data Analytics Center, where students and researchers monitor real-time energy data collected from sensors and smart meters. This hands-on approach not only reduces operational costs but also provides valuable learning opportunities in data-driven sustainability.
Additionally, a green server room has been established with advanced cooling optimization and renewable power integration, lowering the campus’s carbon footprint. These features collectively contribute to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
4. Transport logistcs Campus
The Transport logistics Campus serves as the core of sustainable innovation and renewable energy development within the institute. As part of the Smart Building Implementation strategy, the campus has been designed with a strong focus on energy efficiency, renewable integration, and intelligent resource management.
The entire campus infrastructure operates under a smart microgrid system, integrating solar photovoltaic panels, energy storage batteries, and automated energy distribution units. These systems ensure that electricity generation and consumption are balanced in real time, minimizing energy waste and maximizing renewable utilization.
Buildings are equipped with intelligent HVAC systems, smart lighting with daylight sensors, and digital energy meters to continuously monitor and optimize performance. Research laboratories include IoT-based environmental monitoring tools that track indoor air quality, humidity, and temperature — ensuring optimal conditions for energy experiments.
Moreover, the campus serves as a living laboratory for students and researchers to test sustainable technologies such as smart charging stations, regenerative systems, and AI-based energy optimization algorithms. The Green Energy Research Campus strongly supports SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) by pioneering environmentally responsible building management solutions.
5. Sharda Campus
The Sharda Campus plays a key role in enhancing the daily living experience of students through comfort, safety, and sustainability. Within the framework of the Smart Building Implementation program, the campus has been modernized with intelligent living systems that combine convenience and energy efficiency.
All dormitory buildings are equipped with smart energy meters, automated lighting, and temperature control systems that adjust based on occupancy levels. These technologies significantly reduce unnecessary electricity consumption and ensure an eco-friendly residential environment.
Additionally, smart water management systems have been introduced to monitor usage and detect leaks in real time, helping to conserve water resources. Public areas such as cafeterias, gyms, and study halls are powered by energy-efficient lighting and ventilation systems that maintain optimal comfort with minimal environmental impact.
Safety and well-being are further enhanced through digital access control, CCTV surveillance, and emergency notification systems integrated into a centralized digital network. These innovations reflect the institute’s commitment to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-Being), SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and SDG 13 (Climate Action), ensuring that sustainability extends beyond classrooms into students’ everyday lives.